

Magnesium ribbon placed into copper sulfate solution will result in the formation of a magnesium sulfate solution and the depositing of copper metal. This results in a new salt being formed and the weaker metal coming out of solution and being deposited as a metal precipitate. More reactive metals will displace (push out) less reactive metals from metal salt compounds. Displacement Reactionsĭue to the relative reactivity of metals, given in the reactivity series, when combined they compete to form ionic compounds with other chemicals.

#Metal reactivity series series#
The non-metal elements hydrogen and carbon have been included in the reactivity series as they are often used with metals in experiments and they are also used to help extract metals from their naturally occurring metal ores. These have to undergo chemical processes to extract the pure metal from the ore. are found as copper ore, copper compounds. Students progress at their own pace and you see a leaderboard and live results. It is difficult to separate them from their compounds and extract. Print Share Edit Delete Report an issue Live modes.

#Metal reactivity series free#
The metals at the top of the series (K, Na, Ca, Mg and Al) are so reactive that they are never found in nature as free elements. Gold, for example, can be found in nature as gold metal in rocks as it does not react readily. The metal reactivity series is a list of metals arranged in the order of their decreasing activities. Metals at the top of the series tend to form ions more rapidly than those at the bottom. By comparing the rate at which each metal reacts with water and/or a dilute acid the metals can be placed in order to form the reactivity series. Metals readily react with water and dilute acids, during these reactions hydrogen gas is given off. Metals can be ranked according to their level of reactivity to form the metal reactivity series. Some metals give up their electrons more readily than others and are, therefore, more reactive. Metal ions are positively charged as they lose negative electrons. This means that when they react they tend to lose electrons to form ionic compounds. The less reactive metal is a better electron acceptor than the more reactive metal, thus the less reactive metal is reduced.Metal elements have either 1,2 or 3 electrons in their outer electron orbits.This is because more reactive metals lose electrons and form ions more readily than less reactive metals, making them better reducing agents.
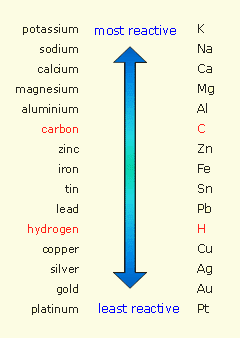
Any metal will displace another metal that is below it in the reactivity series from a solution of one of its salts.The reducing agent in the reaction is magnesium:Ĭopper oxide + magnesium → copper + magnesium oxideĭisplacement reactions between metals and aqueous solutions of metal salts.The less reactive metal, in this case copper, ends up in elemental form as it is reduced.As magnesium is above copper in the reactivity series, magnesium is more reactive so can displace copper from its oxide.2) This element, which takes its name from the. It is possible to reduce copper(II) oxide by heating it with magnesium 1) When this metal reacts with cold water, the hydrogen gas that is produced burns with a yellow flame (6).This means that a more reactive metal can displace a less reactive metal from its oxide by heating.The reactivity of metals increases going up the reactivity series.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
